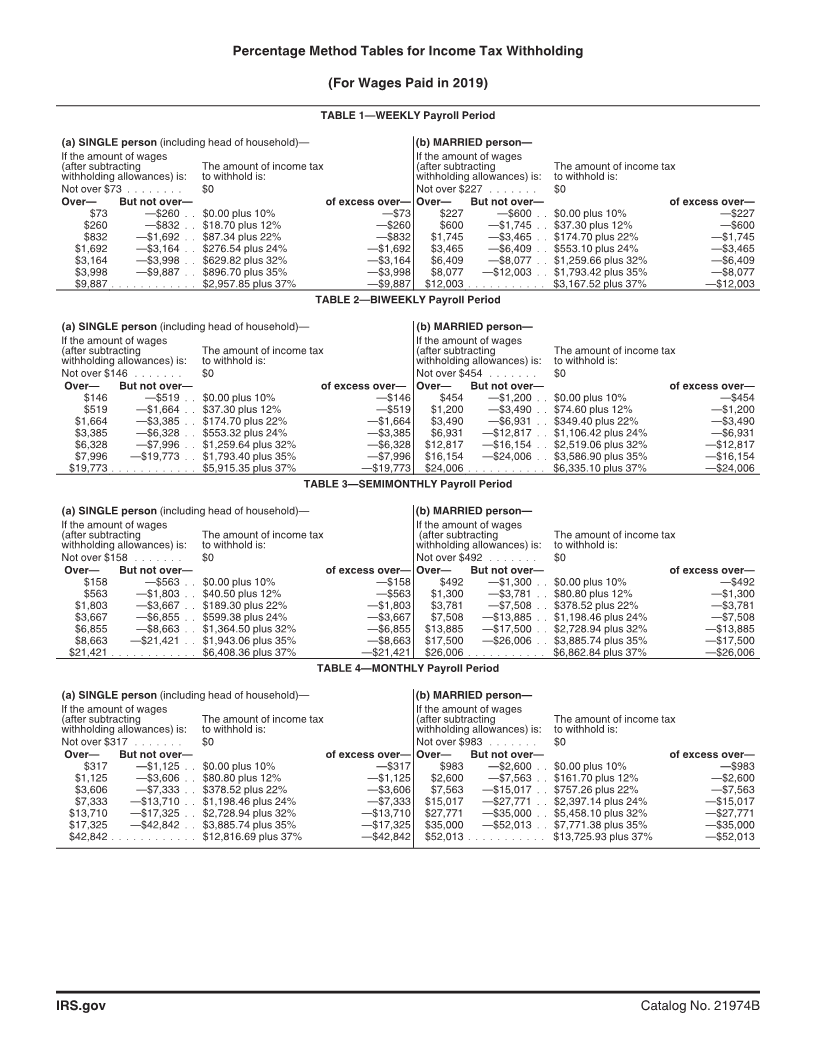
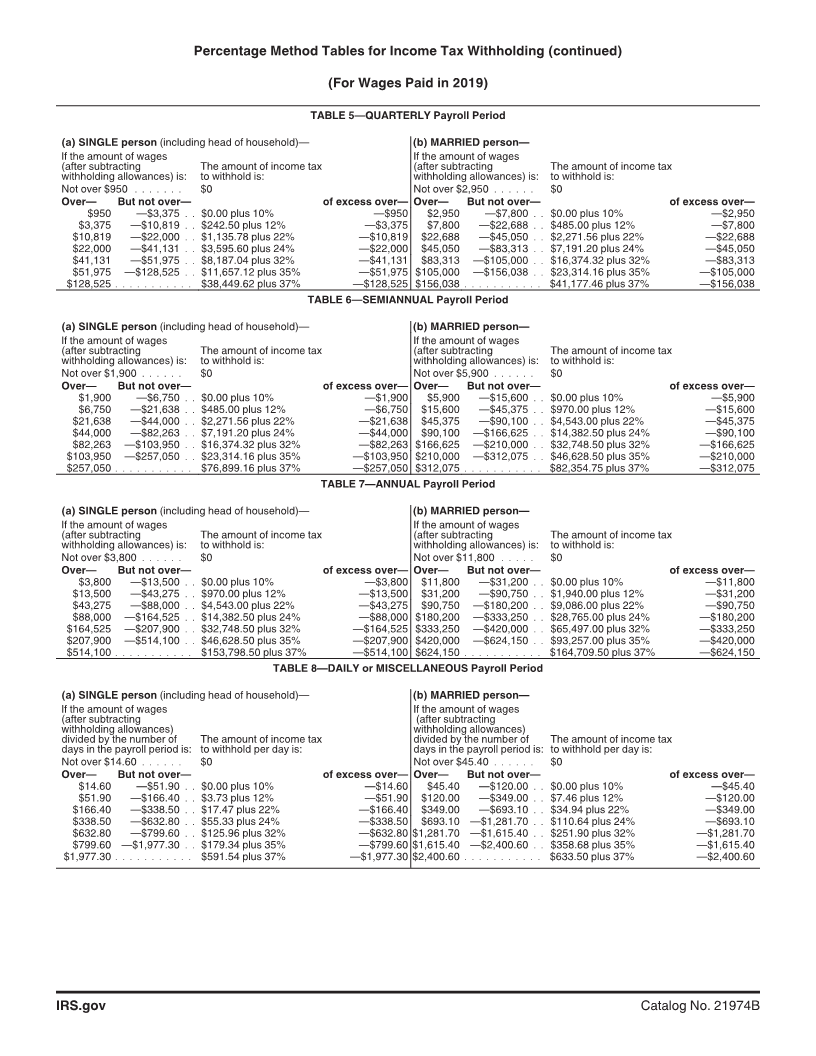
Enlarge image
Userid: CPM Schema: Leadpct: 100% Pt. size: 10 Draft Ok to Print
notice
Fileid: … es/N1036/201812/A/XML/Cycle04/source (Init. & Date) _______
AH XSL/XML
Page 1 of 4 8:54 - 3-Dec-2018
The type and rule above prints on all proofs including departmental reproduction proofs. MUST be removed before printing.
Department of the Treasury
Notice 1036 Internal Revenue Service
(Rev. December 2018)
Early Release Copies of the 2019 Note. Nonresident alien students from India and
business apprentices from India aren't subject to this
Percentage Method Tables for procedure.
Income Tax Withholding
Instructions. To figure how much income tax to
withhold from the wages paid to a nonresident alien
Future Developments
employee performing services in the United States, use
For the latest information about developments related to the following steps.
Notice 1036, such as legislation enacted after it was Step 1. Add to the wages paid to the nonresident
published, go to IRS.gov/Notice1036. alien employee for the payroll period the amount shown
in the chart below for the applicable payroll period.
Percentage Method Tables for
Income Tax Withholding Amount To Add to Nonresident Alien Employee's
Wages for Calculating Income Tax Withholding
Attached are early release copies of the Percentage Only
Method Tables for Income Tax Withholding that will
appear in Pub. 15, Employer's Tax Guide (For use in Payroll Period Add Additional
2019). Pub. 15 will be posted on IRS.gov in December Weekly $ 153.80
2018. Biweekly 307.70
The wage amounts shown in the Percentage Method Semimonthly 333.30
Tables for Income Tax Withholding are net wages after
Monthly 666.70
the deduction for total withholding allowances. The
withholding allowance amounts by payroll period have Quarterly 2,000.00
changed. For 2019, they are: Semiannually 4,000.00
One Withholding Annually 8,000.00
Payroll Period Allowance
Daily or Miscellaneous 30.80
Weekly $ 80.80 (each day of the payroll period)
Biweekly 161.50
Semimonthly 175.00 Step 2. Use the amount figured in Step 1 and the
number of withholding allowances claimed (generally
Monthly 350.00 limited to one allowance) to figure income tax
Quarterly 1,050.00 withholding. Determine the value of withholding
allowances by multiplying the number of withholding
Semiannually 2,100.00
allowances claimed by the appropriate amount in the
Annually 4,200.00 first table shown earlier. Reduce the amount figured in
Daily or Miscellaneous 16.20 Step 1 by the value of withholding allowances and use
(each day of the payroll period) that reduced amount to determine the wages subject to
income tax withholding. Figure the income tax
withholding using the Percentage Method Tables for
When employers use the Percentage Method Tables for Income Tax Withholding provided on pages 3 and 4.
Income Tax Withholding, the tax for the pay period may Alternatively, you can figure the income tax withholding
be rounded to the nearest dollar. If rounding is used, it using the Wage Bracket Method Tables for Income Tax
must be used consistently. Withheld tax amounts should Withholding included in Pub. 15 (For use in 2019).
be rounded to the nearest whole dollar by dropping
amounts under 50 cents and increasing amounts from
50 to 99 cents to the next dollar. For example, $2.30 Social Security and Medicare Tax for
becomes $2 and $2.50 becomes $3. 2019
For social security, the tax rate is 6.2% each for the
Withholding Adjustment for employee and employer, unchanged from 2018. The
Nonresident Aliens social security wage base limit is $132,900. The
Medicare tax rate is 1.45% each for the employee and
For 2019, apply the procedure discussed next to figure employer, unchanged from 2018. There is no wage base
the amount of income tax to withhold from the wages of limit for Medicare tax.
nonresident alien employees performing services within
the United States.
IRS.gov Catalog No. 21974B